The Significance of Earth Science and Its Key Disciplines
The Significance of Earth Science and Its Key Disciplines
Earth sciences play a vital role in helping us understand our planet's dynamic systems, from weather patterns to tectonic activities. By studying Earth’s structure, processes, and history, we gain insights into critical global challenges like climate change, natural disasters, and resource management. As we face growing environmental and societal issues, Earth science provides a foundation for solutions that ensure sustainability and safety for future generations, along with other branches of Earth science that contribute to our understanding . This article explores the significance of Earth science and its key disciplines, including various branches of earth science, that shape our understanding of the world.
Earth science, often called the science of the Earth, is a fascinating field that covers the study of everything from rocks beneath our feet to the atmosphere high above us, and even the solar system and other planets. Earth scientists dedicate their careers to exploring the various processes that shape our world and affect all living things. With several branches of Earth science and other branches to explor , this discipline allows us to understand not only our planet but also the entire universe. By exploring natural hazards, resources, and climate change, earth sciences influence many lives around the globe.
In a time where environmental degradation and resource scarcity are on the rise, Earth science equips us with the tools and knowledge needed to respond effectively. From satellite imaging that monitors deforestation to seismographic networks that predict earthquakes, Earth science supports real-world applications that save lives and improve living conditions. It also nurtures curiosity about the natural world, encouraging new generations of scientists and researchers to ask big questions and explore groundbreaking solutions. The integration of Earth science into education, policymaking, and innovation highlights its importance not just for scientists, but for everyone invested in the future of our planet.
Understanding Earth Science and Its Role in Modern Knowledge
So, what is Earth science? It’s the comprehensive study of our planet, encompassing physical, chemical, and biological processes that shape its structure and environment. Earth sciences involve the investigation of the solid earth, its atmosphere, oceans, and outer space. Earth sciences bridge the gap between theoretical understanding and practical application, helping humanity navigate and mitigate the planet's most pressing challenges. These sciences also focus on the physical properties of earth's surface and explore how processes like volcanic eruptions and erosion alter the planet over time.
Earth and space science go hand in hand, offering insights into both terrestrial and extraterrestrial phenomena, from ocean currents to planetary evolution. Earth scientists study these aspects to make sense of air masses, climate patterns, and the dynamic processes that define our solar system. By analyzing Earth in the context of the broader universe, scientists can develop models to predict climate patterns, tectonic movements, and even the potential for life beyond our planet. Earth scientists continually update their understanding of the physical geology and atmospheric science that govern natural events.
Earth sciences also guide the responsible use of natural resources, including fossil fuels and minerals, ensuring that humans can sustain life while minimizing harm to the environment. Understanding the structural geology and geologic time scale enables us to track how earth’s crust evolved, supporting modern extraction methods. The study of earth's spheres—the lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere—helps scientists determine how these systems interact and influence our lives. These foundational elements are introduced early in the high school Earth science curriculum to build a comprehensive understanding.
Earth sciences also contribute to the discovery of new energy resources, such as geothermal energy, which comes from the earth’s core. With climate change becoming a pressing global issue, studying various processes related to earth's atmosphere, water vapor, carbon dioxide levels, and climate patterns allows scientists to forecast future environmental changes. These aspects of Earth sciences touch almost every important aspect of human life, including living creatures from food production and energy consumption to water availability and health. Earth sciences emphasize the impact of geologic hazards and the need for sustainable development.

The role of Earth sciences in modern knowledge includes:
Predicting Natural Disasters
Earth scientists study fault lines, volcanic activity, and weather systems to forecast disasters like earthquakes, tsunamis, hurricanes, and floods. These efforts help reduce the impact of natural hazards on many lives. Early warning systems have saved countless lives by providing critical lead time for evacuation and preparation. Additionally, predictive models are constantly evolving through AI and machine learning, offering more accurate forecasts. These tools enable governments and local communities to plan ahead and minimize economic damage, reduce casualties, and ensure that emergency resources are deployed efficiently. Earth sciences play a crucial role in understanding seismic activity, the composition of the earth’s structure, and upper atmosphere interactions.Managing Natural Resources
By understanding geological formations and hydrological cycles, Earth science helps identify and manage natural resources such as water, minerals, and fossil fuels. Sustainable resource extraction and conservation efforts rely heavily on this field. Earth scientists also help in locating renewable energy sources like geothermal reservoirs and assessing groundwater availability in drought-prone regions. This role is especially critical as nations seek to transition from fossil fuels to clean energy, requiring a balanced approach to resource usage and environmental protection. Earth sciences also emphasize the importance of studying the physical and chemical aspects of minerals, rocks, and water chemistry.Understanding Environmental Changes
Earth science is essential for monitoring global changes, including deforestation, desertification, and rising sea levels. Satellite imagery, climate models, and atmospheric studies enable us to detect shifts and plan mitigation strategies. It allows scientists to track greenhouse gas concentrations, study melting glaciers, and examine the impact of human activities on ecosystems. This understanding is vital for framing international policies such as the Paris Agreement and for guiding nations in building resilience against future environmental risks. Earth sciences, through their many branches, provide insights into oceans, atmosphere, and earth's history, aiding in global environmental preservation.Supporting Sustainable Development
Whether it's constructing earthquake-resistant buildings or developing clean energy sources, Earth science plays a key role in sustainable development. Policies rooted in scientific understanding promote balanced growth that respects environmental boundaries. Earth scientists contribute to urban planning, sustainable agriculture, and eco-friendly infrastructure design. Their work ensures that developmental projects are not only economically viable but also environmentally sound. Through environmental impact assessments and sustainability audits, Earth science continues to shape a future where growth and preservation go hand in hand. The study of other branches such as marine geology, oceanography, and oceanographers study support climate resilience and water conservation efforts across the world.
Earth sciences unite several branches of scientific study, covering everything from volcanoes and earthquakes to the moon, life, and other planets. Earth scientists focus on how our planet connects with the entire universe, exploring living creatures, living things, and ecosystems. Earth sciences gave rise to some of the most significant scientific disciplines, including geology, physics, chemistry, biology, and atmospheric science, offering unlimited access to planetary knowledge and tools that help preserve human life and our world.
The Four Key Branches of Earth Science
What are the four branches of Earth science? They are:
1. Geology – The Study of Earth's Solid Materials
Geology delves into the Earth’s solid structure, from rocks and minerals to tectonic plate movements, including the study of volcanoes . It explores processes like erosion, sedimentation, and volcanic activity. Geologists study the formation of mountain ranges, earthquakes, and fossil records to understand Earth’s past and predict its future.
Applications:
Locating natural resources like oil and gas
Predicting earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
Supporting construction projects through geotechnical analysis
Fun Fact: The theory of plate tectonics, which explains the movement of Earth’s continents, was only widely accepted in the 1960s.
Geology also plays a key role in archaeological discoveries and dating ancient civilizations. Techniques such as radiometric dating allow us to determine the age of rocks and fossils, unraveling the timeline of earth's history and geological events. Geologists work closely with engineers to evaluate soil stability and rock composition before construction projects, ensuring safe infrastructure. In a world increasingly impacted by land degradation, geological surveys inform land-use planning and natural disaster prevention.
2. Meteorology – The Study of Weather and Atmosphere
Meteorology focuses on atmospheric phenomena and weather patterns. Meteorology plays an important aspect in weather forecasting, climate monitoring, and the study of extreme events like hurricanes and droughts.
Applications:
Daily weather forecasts
Climate change research
Aviation safety and planning
Interesting Stat: The global weather forecasting market is projected to exceed $4.6 billion by 2027.
Meteorologists gather physical data from satellites, radars, and weather balloons to make precise forecasts. Their work influences multiple sectors, including agriculture, transportation, and tourism. From issuing heatwave warnings to analyzing global warming trends, meteorology is critical in adapting to climate change. It also helps in designing climate-resilient infrastructure and improving early warning systems for extreme weather events, which are becoming more frequent and severe due to global warming.
3. Oceanography – The Exploration of Oceans
Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans, covering marine life, ocean currents, and seabed geology. With oceans covering more than 70% of the Earth’s surface, this discipline is vital for understanding global climate and biodiversity.
Applications:
Marine ecosystem conservation
Tsunami warning systems
Studying ocean currents that influence climate (e.g., El Niño)
Fact: Oceans absorb about 30% of carbon dioxide emissions and produce over 50% of the Earth’s oxygen.
Oceanography also examines the impact of human activity on marine environments, such as plastic pollution, oil spills, and coral bleaching. This field integrates biology, chemistry, and geology to better understand how ocean systems work, and oceanographers study the impact of these systems on global climate . Oceanographers also study the deep sea—an area still largely unexplored—to identify new species and understand Earth's geological history. Advances in this field contribute to sustainable fisheries, biodiversity protection, and the blue economy.
4. Astronomy – The Study of Celestial Bodies
Though often considered separate from traditional Earth science, astronomy connects us to the cosmos and helps contextualize Earth’s place in the universe. Astronomy contributes to our understanding of planetary formation, including the moon's role, solar radiation, and the potential threats from space.
Applications:
Studying the Sun’s effect on Earth’s climate
Tracking asteroids and comets
Supporting satellite-based Earth observation
Fun Insight: The James Webb Space Telescope helps scientists peer into the earliest stages of galaxy formation and may also offer new data about Earth-like planets.
Astronomy also enhances our understanding of time, navigation, and energy. The study of solar flares and cosmic radiation, along with the composition of celestial bodies, helps protect astronauts and satellite technology. It informs innovations in solar energy harvesting and contributes to space weather prediction, which is vital for GPS and communication systems. With private space exploration on the rise, astronomy and space science are more relevant than ever in addressing both Earth-bound and extraterrestrial challenges.
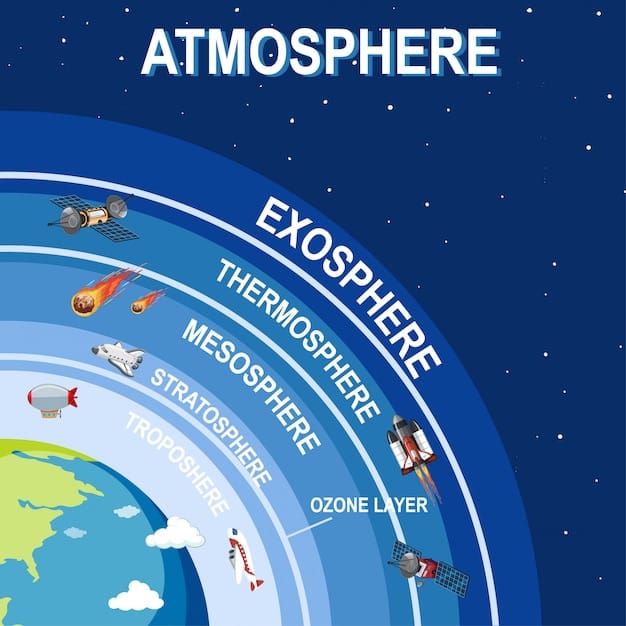
Examples of Earth Science in Everyday Life
You might be surprised at how often we encounter Earth science in daily life. It silently operates in the background, influencing decisions, shaping environments, and keeping us safe:
Weather Forecasts
Every time we check the weather before leaving the house, we are benefiting from meteorology. Forecasts influence travel plans, clothing choices, and agricultural activities. Accurate weather data helps airlines plan safer flight paths and informs farmers when to plant or harvest crops. It also helps city planners prepare for extreme weather events like heatwaves or snowfall.Earthquake Alerts
Geology-based systems detect seismic activity and issue alerts that can minimize casualties and infrastructure damage. Mobile apps and early warning systems have made it possible for people to receive real-time alerts, giving them precious seconds to take shelter. These alerts have already saved lives in regions prone to earthquakes such as Japan and California.Understanding Tides and Marine Life
Oceanography informs us about tidal patterns, essential for navigation, fishing, and coastal development. It helps protect marine biodiversity and supports aquaculture by providing insights into ocean temperatures and salinity. Recreational activities like surfing and boating also rely on tidal data.Climate Monitoring via Satellites
Earth and space science collaborates to monitor polar ice melt, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions, supporting global climate agreements. These technologies also help track air quality, urban heat islands, and rising sea levels. Such data plays a key role in international climate negotiations and disaster preparedness.Building Infrastructure
Construction projects rely on geotechnical reports and environmental assessments to ensure safety and sustainability. Engineers assess soil conditions and groundwater levels before laying foundations, preventing structural failures. Earth scientists also evaluate flood risk and seismic hazards during city planning.Disaster Preparedness and Emergency Response
Earth scientists design risk maps and hazard zones to guide urban planning and disaster readiness. These maps are vital for insurance companies, emergency responders, and local governments. They help allocate resources efficiently and ensure that rescue operations are swift and effective.
Conclusion
In summary, Earth sciences are fundamental to understanding and preserving our planet. With its diverse disciplines, Earth science connects various fields of study to address environmental, economic, and societal challenges. From forecasting storms to tracking resource use, Earth science is deeply intertwined with our daily lives and long-term survival, reflecting the true scope of what is Earth science.
An early introduction to Earth science is essential for students and researchers to build a sustainable and informed future. As technology advances, so too does our ability to understand and protect the Earth. Whether it’s through satellites, fieldwork, or simulations, including the study of air masses Earth science empowers us to become better stewards of the planet through practical applications of Earth and space science.
Earth science is more than just a subject—it’s a powerful tool for understanding our world and making it better. From the structure of the earth’s core to the movements of the upper atmosphere and ocean currents, earth sciences offer a rich, detailed view of the planet we call home. With knowledge from many branches of science, including geology, physics, chemistry, and biology, earth scientists continue to expand our understanding of the Earth and beyond.
As we face growing environmental challenges and explore the solar system and other planets, earth sciences will remain at the forefront of innovation and discovery. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or simply curious about the world, diving into the world of earth science opens the door to endless possibilities.
So next time you look up at the sky, walk on the ground, or watch the waves—remember, there's a science that connects it all. And that science is Earth Science.
Earth Science – FAQs
1. What are Earth sciences, and why are they important for understanding our planet?
Earth sciences study the physical, chemical, and biological processes of our planet, helping us understand phenomena like earthquakes, volcanoes, and climate change. They are crucial for environmental awareness, disaster mitigation, and resource management. Additionally, earth sciences examine the planet’s structure and composition, from the earth’s core to the upper atmosphere. They explore natural resources and minerals related to geologic hazards, helping scientists develop strategies to preserve ecosystems and protect human life. This field of science also supports technological advancement by providing knowledge about processes that occur in the earth’s crust, atmosphere, and oceans.
2. How does Earth and space science help us study climate change and planetary evolution?
Earth and space science provide tools to monitor Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land. They also offer insights into how other planets evolve, allowing for comparative understanding of Earth's past, present, and potential future. These sciences help identify climate patterns and the effects of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases on global temperatures. They also offer models to predict climate change and study the impacts of natural disasters. Understanding planetary evolution provides clues about Earth’s geologic history and how atmospheric science can explain shifts in weather patterns and other environmental phenomena.
3. What are some real-world examples of Earth science that impact daily life?
Everyday examples include weather forecasts, tsunami warnings, pollution tracking, and resource management. These services rely on Earth science research to keep societies informed and safe. Earth scientists also study the effects of natural hazards on earth's surface and provide data on seismic activity, volcanic eruptions, and ocean currents. These efforts support urban planning, emergency preparedness, and environmental conservation. By analyzing physical properties of materials, understanding water chemistry, and assessing air masses, earth sciences impact our ability to adapt to natural challenges and maintain sustainable living conditions for all.
4. How does the high school Earth science curriculum prepare students for future careers?
The high school Earth science curriculum introduces students to geology, including physical geology meteorology, oceanography, and astronomy. It builds foundational knowledge for careers in research, environmental management, policy-making, engineering, and space exploration. Through hands-on experiences, students learn about plate tectonics, structural geology, and the composition of the earth's crust. They explore the chemistry of oceans, the physics of the atmosphere, and the role of energy resources. These experiences provide insight into earth scientists’ work and prepare students to pursue studies in fields like atmospheric science, marine geology, and natural resource conservation.
5. Why is an introduction to Earth science essential for students and researchers?
An introduction to Earth science builds critical thinking skills, promotes environmental stewardship, and prepares students to tackle global challenges through informed scientific approaches. It lays the groundwork for innovative solutions in a rapidly changing world. Understanding earth’s structure, ocean currents, and weather patterns helps develop a holistic view of our planet. The study of earth sciences also fosters appreciation for the many branches of science that support human life. Whether examining the earth's atmosphere, fossil fuels, or earth's history through geologic time, this knowledge supports future discoveries in climate science, geology, and space exploration.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted